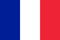
Osteochondrosis is commonly referred to as dystrophic changes in the bone and connective tissue of the spine. The spine cannot cope with normal loads - and this is expressed above all in the occurrence of pain, which is not particularly pronounced at first, but becomes stronger over time.
The main symptoms of the disease
Thoracic osteochondrosis is a disease that usually occurs in adulthood and does not fully manifest itself for a long time. This is because the thoracic spine naturally supports and fixes the ribs - this protects the intervertebral discs well.

The nucleus of the intervertebral disc with this disease becomes thinner and dries up, the fibrous tissue around it begins to collapse, the cartilaginous tissue undergoes negative changes. The spine cannot cope with normal loads - and this is expressed above all in the occurrence of pain, which is not particularly pronounced at first, but becomes stronger over time. With significant loads - a sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, constant stress, poor posture and back injuries, osteochondrosis sooner or later affects the chest region. The disease is considered very common - every third adult suffers from it.
What are the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis? First of all, when pain occurs, which include:
- interscapular and intercostal neuralgic shootouts;
- pain in left side of chest;
- pain in arms aggravated by lifting and grasping to fingertips;
- pain when bending over;
In addition, thoracic osteochondrosis can manifest itself as numbness - not only in the chest, but also in various parts of the body. Sometimes osteochondrosis leads to speech disorders, sometimes even scaly skin, brittle nails, itchy skin and indigestion.
Pain in osteochondrosis of the chest can manifest itself in different ways. Sometimes these are light stabbing or dull pains that appear in the late afternoon and disappear after physical activity - for example, a short walk. As a rule, this is how the initial stage of thoracic osteochondrosis proceeds, when the intervertebral discs are not yet deeply affected.
In later stages of the development of the disease, symptoms of pain often manifest themselves in the form of lumbago. The pain is pronounced, acute, disrupts normal breathing, and unnecessary movements only aggravate the situation. Back pain often begins after a long period of inactivity - for example, after working in a static position at the computer for several hours.
The special "cunning" of osteochondrosis of the chest region is that the disease can skillfully disguise itself as a dozen other ailments. Osteochondrosis of the chest is very easy to confuse with symptoms of pneumonia, angina pectoris, ischemia, myocardial infarction. Sometimes the disease is more similarrenal or hepatic colic, and speech disorders and numbness in various parts of the body are even mistaken for signs of a stroke.
Moreover, the mistake is made not only by the patients themselves, but also by experienced doctors - which greatly complicates the diagnosis of the disease. Breast osteochondrosis is particularly difficult to detect in its early stages - which is why it is often diagnosed when the disease is already established and has progressed to the chronic stage.
Meanwhile, the timely diagnosis of thoracic osteochondrosis is of fundamental importance. This allows you to immediately start treatment and delay the development of the disease, which will significantly stop the pain symptoms associated with the disease.
How dangerous is osteochondrosis of the chest region?
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine does not pose an immediate threat to the life of the patient. However, in a neglected condition, there can be significant complications:
- the appearance of chronic intercostal neuralgia;
- hernia of the thoracic region;
- Compression of the spinal cord in the damaged area of the spine.
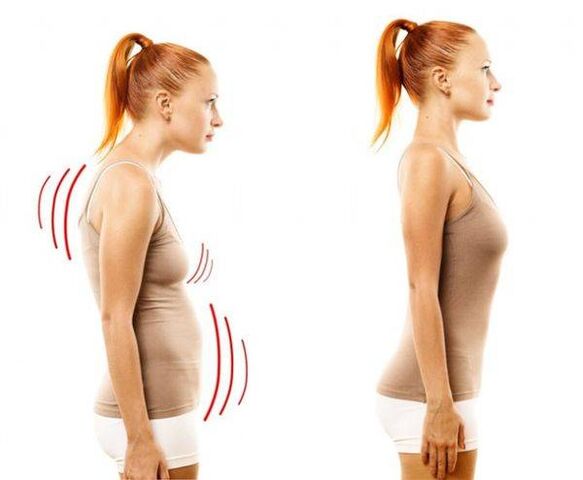
The started osteochondrosis of the spine is manifested by scoliosis, sometimes the disease passes to the cervical vertebrae, causing loss of voice.
In addition, a strong weakening of the spine in the chest area can lead to deformation of the internal organs of the peritoneum. This in turn can lead to all sorts of diseases of the digestive tract - stomach, pancreas, liver, kidneys, bile ducts.
Thoracic osteochondrosis requires careful treatment, which will help slow down the development of the disease for a long time, avoid complications - and completely neutralize the symptoms of the disease in the early stages.
How is the disease treated?
What methods are used in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis? First, a thorough diagnosis is carried out, which includes both a specialist medical examination of the patient and examinations with modern equipment. This allows you to accurately diagnose and make sure that it is osteochondrosis, and not some other disease.
After the diagnosis, the doctor can use the following therapy methods:
- Medicines to relieve pain symptoms;
- physiotherapy, laser therapy, acupuncture and reflexology;
- manual therapy and therapeutic massage;
- a special course of medical gymnastics.
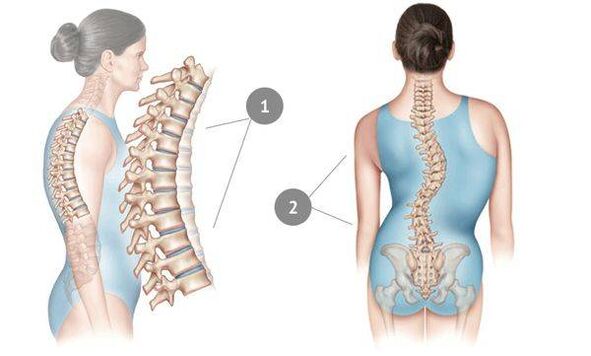
Almost all of these methods are aimed not at eliminating osteochondrosis as such, but at relieving inflammation and reducing the severity of pain. The elimination of pain is the main goal of the treatment of osteochondrosis of the chest. At the same time, manual therapy and exercise therapy can "straighten" the spine, increase the distance between the vertebrae and prevent compression. However, the patient must regularly perform therapeutic exercises, otherwise there will be no result.
In some, especially severe cases, surgical treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis can be used. In such a situation, the affected vertebrae are replaced with a prosthesis - practice shows that the operation is successful in about 50% of patients.
Regular spa stays are recommended for thoracic osteochondrosis. In sanatorium conditions, the patient receives a full-fledged complex therapy combining drugs, physiotherapy and gymnastic methods - and for a long time feels a significant improvement in his condition.
home remedies
In the acute course of the disease, it is recommended to treat thoracic osteochondrosis in hospital. But if the symptoms are mild, then there is no need to go to the hospital. In this case, home care is fundamental. It is not only possible, but also necessary to treat osteochondrosis with folk remedies - sometimes they show no less effectiveness than official medical procedures.
Home treatment is aimed at the same goal - the rapid elimination of pain and inflammation and the reduction of the symptoms of the disease. Therefore, in the treatment of osteochondrosis with folk remedies, decoctions, ointments, compresses and infusions of herbs and plants are used, which have a sedative, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
What medicinal preparations are recommended instead of tea and drinks with osteochondrosis? These are chamomile, calendula, sage, birch leaves, strawberry leaves and ripe viburnum. In addition, these fees can be mixed among themselves - a fragrant hot drink from two or three different herbs gives a noticeable effect.
Decoctions are brewed like tea - a tablespoon of a medicinal plant is poured into a glass of hot water, infused and consumed inside 2-3 times a day. Simultaneously with taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory herbs, it is recommended to drink soothing infusions of motherwort, lavender, valerian - stress, which is inevitable in the course of the disease, can further aggravate the symptoms.
In addition to medicinal decoctions, baths with medicinal additives are used - for example, extracts of celandine, plantain and pine needles have a soothing and warming effect. Such a bath relieves muscle spasms, improves blood circulation between the inflamed discs of the spine and eliminates inflammation.
Compresses, ointments and rubs are not recommended for acute pain. However, they can be used during a lull in the disease. For example, rubbing with mustard-camphor ointment is popular – 50 grams of mustard and camphor are diluted with 100 milliliters of alcohol and 100 grams of raw egg white and stirred until smooth. The ointment is applied to the back at night for two weeks - the treated area must be covered with a woolen cloth on top.
What to do in the event of an exacerbation?
What is considered an exacerbation of the disease? This term refers to intense pain sensations. If the patient feels noticeable discomfort, known back pain and dull pain in the chest area, radiating to the peritoneum, lower back and arms, it is time to pay maximum attention to your disease.
During an exacerbation it is recommended:
- avoid hypothermia and stress;
- be as little as possible in still poses in which the load on the spine is maintained;
- apply sparing compresses and ointments to the affected area, which do not act too harshly;
- gently massage the affected areas yourself - but avoid strong pressure;
- to continue physical therapy exercises to the best of your ability - but only if this does not lead to increased pain.
In the case of acute complications, bed rest is also recommended. If the pain is unbearable, hospitalization can even be carried out. However, in most cases, exacerbations of thoracic osteochondrosis can be stopped at home, especially if you combine a sparing regime with taking medications prescribed by a specialist.
The main condition for the exacerbation of osteochondrosis is the lack of physical activity. Inflamed intervertebral discs need maximum rest - then it is possible to quickly cope with the exacerbation.